Bloom’s Taxonomy
Are you trying to teach people without identifying educational objectives? If you keep doing that, your learners may waste their time succeeding in things that are of no use to them. To avoid that, clarify your instructional goals using Bloom’s Taxonomy.
This article will help you learn:
- What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
- Original Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Bloom’s Taxonomy levels
- Why Bloom’s Taxonomy is important?
- Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy attempts to classify learning stages from remembering facts to creating new ideas based on the acquired knowledge.
The idea of Bloom’s Taxonomy is that learning is a consecutive process. Before applying a concept in real life, we must understand it. Before we understand a concept, we must remember the key facts related to it.
Although initially described as a framework, it is now often depicted as a pyramid.
The basis of the pyramid is Knowledge, the first level of learning. Above it lies Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis and Evaluation. Each level above builds upon the one below, so you can only move up the pyramid one step at a time.
In the context of employee learning and development, Bloom’s Taxonomy guides corporate training by focusing on critical thinking over simple memorization. Created in 1956 and updated in 2001, it helps trainers design programs that teach employees to think deeply and solve problems effectively, matching today’s fast-paced work environments.
Now, we are diving into both versions and see how they apply to our learning strategies.
Original Bloom’s Taxonomy
The original taxonomy was first described in 1956 in the book Taxonomy of Educational Objectives by American educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom and his coauthors Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl. Their book classifies learning goals into one of the categories mentioned above (from Knowledge to Evaluation).
Their goal was to provide teachers with a common vocabulary to discuss curricular and evaluation problems with greater precision.

Training evaluation form
Get a handy printable form for evaluating training and course experiences.
Learn moreThe taxonomy of educational objectives was supposed to help teachers speak the same language and thus “facilitate the exchange of information about their curricular developments and evaluation devices.”
Though it was designed primarily for college professors, it finally became popular among educators, from K-12 teachers to corporate trainers.
Since its publication, the book has been translated into more than twenty languages and is now used for instructional design worldwide. However, it is currently more often applied in its revised version.
Comparison image of the original vs. revised Bloom’s Taxonomies
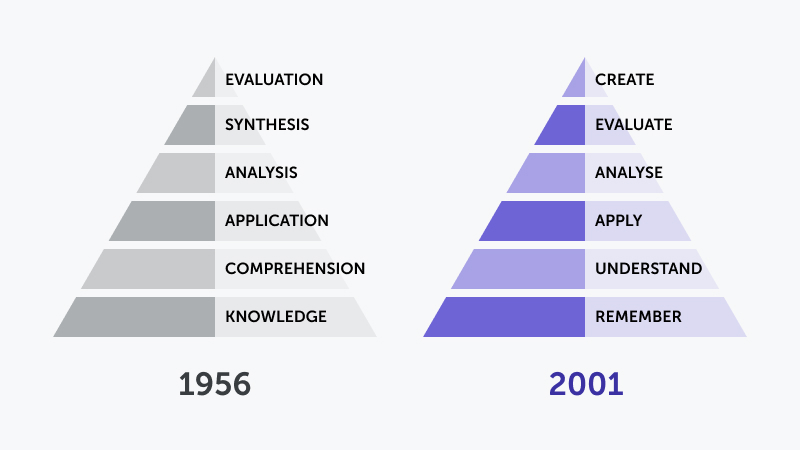
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
To provide learners with clearer instructional goals, a group of researchers led by Bloom’s colleague David Krathwohl and one of Bloom’s students, Lorin Anderson, revised the taxonomy in 2001.
In the new variant, nouns were replaced by action verbs. Also, the two highest levels of the taxonomy were swapped. The new learning stages are Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate and Create. The authors also defined cognitive processes associated with these instructional goals. For example, the ability to remember requires recognizing and recalling.
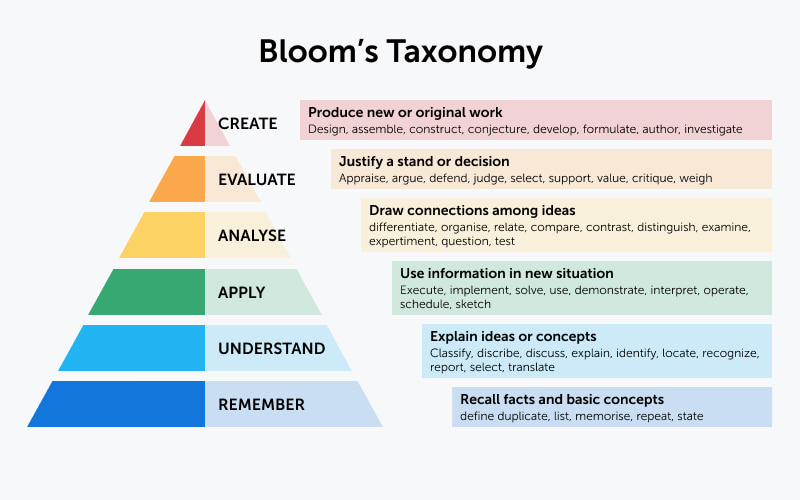
Bloom’s Taxonomy levels
Let’s take a closer look at each learning stage, based on the book describing the revised framework A Taxonomy For Learning, Teaching and Assessing by Krahtwohl and Anderson. The authors recommend reading the name of each learning category as though preceded by the phrase “The student is able to…” or “The student learns to…”
1. Remember
This stage of learning is about memorizing basic facts, dates, events, persons, places, concepts and patterns.
In corporate training, remembering is about memorizing key company facts, product details, compliance rules, or standard operating procedures. For example, learners might be asked to recall:
- The core values of the company.
- Safety protocols for their work environment.
- Key product features and benefits.
This stage involves recognizing (product names, or safety signs from memory) and recalling (memorizing and retrieving important company policies or product information).
2. Understand
Understanding in a corporate setting moves learners beyond rote memorization, encouraging them to explain concepts in their own words or interpret data. Examples include:
- Describing the impact of a new policy on daily operations.
- Interpreting a sales graph to summarize quarterly performance.
Key processes here include:
- interpreting data,
- exemplifying through case studies,
- classifying types of customer feedback,
- summarizing project reports,
- inferring conclusions from meeting discussions,
- comparing different leadership styles,
- and explaining the rationale behind strategic decisions.
3. Apply
Now, it’s time to use learned information in new but related contexts, such as solving problems or executing tasks based on training.
Corporate learners might be tasked with:
- Applying a new sales technique in a role-play scenario.
- Using a software tool to manage customer relationships.
This stage emphasizes executing (following a procedure for a familiar task) and implementing (applying a procedure in a new context).
4. Analyze
Analysis in corporate training entails breaking down complex information or processes to understand their components and relationships.
Learners might:
- Analyze sales data to identify trends.
- Examine a project’s failure to pinpoint contributing factors.
Activities focus on differentiating between relevant and irrelevant data, organizing parts of a project to outline its structure, and attributing causes to an outcome, such as determining the factors leading to a successful product launch.

Training evaluation form
Get a handy printable form for evaluating training and course experiences.
Learn more5. Evaluate
Evaluation requires judgment and critical thinking to assess the value or effectiveness of something, based on criteria and standards. In a corporate environment, this could involve:
- Assessing the feasibility of a new market expansion plan.
- Critiquing a proposed project management approach.
Learners engage in checking (evaluating the consistency of an argument) and critiquing (judging a proposal against set criteria).
6. Create
Creation, the pinnacle of Bloom’s Taxonomy, entails producing something new or original. This stage is vital for innovation within the company. Examples include:
- Designing a marketing strategy for a new product.
- Developing a training program for new hires.
Key cognitive processes are generating (coming up with a new business strategy), planning (outlining a project plan), and producing (creating a new product design).
Why Bloom’s Taxonomy is important
Bloom’s Taxonomy can help educators map learning within a single lesson or even a whole course.
Using the taxonomy as a guide, trainers can identify clear instructional goals corresponding to each taxonomy level and create plans to achieve them.
By setting achievable objectives for learners, instructors make them more active and responsible for their education.
The taxonomy can also be useful for evaluating learners correctly.
For L&D professionals and instructional designers, applying Bloom’s Taxonomy to corporate training programs ensures not just the acquisition of knowledge, but the development of skills that enhance employees’ ability to innovate, solve problems, and make informed decisions, driving business success and personal growth.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs
When talking about Bloom’s taxonomy, action verbs associated with the categories and cognitive processes are often mentioned. Instructors use these verbs to describe activities required for achieving educational objectives corresponding to each level.
For instance, at the analyzing level, the Azusa Pacific University recommends using verbs like “compare”, “distinguish”, and “simplify” when formulating instructional tasks.
There is a list of Bloom’s taxonomy verbs, created by the University of Arkansas. Using these verbs can help learners explicitly navigate what they must do to demonstrate their mastery of the objective.
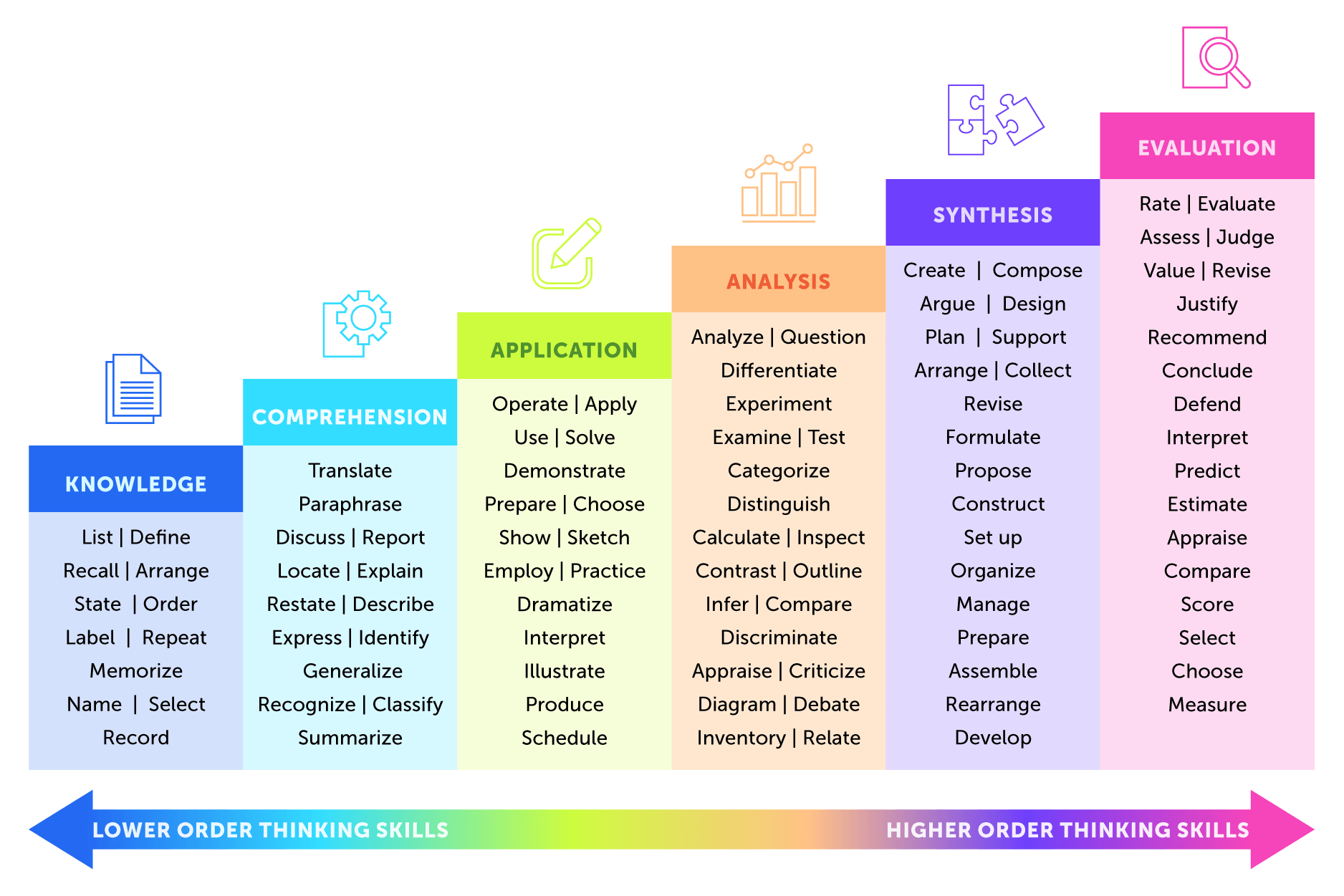
However, neither Bloom’s original book nor his followers’ book contains a list of such verbs. The authors of a study of 47 verb lists collected from 35 universities and textbooks note: “There was very little agreement between these lists, most of which were not supported by evidence explaining where the verbs came from.”
Nevertheless, given that such lists of verbs are being created anyway, the authors identified verbs that appeared in more than 50% of the listings. Then they identified verbs for which 50% of their appearances were in one specific tier. Using these verbs, the authors constructed “A Master List of Action Verbs for Learning Outcomes.”



