Cybersecurity training
Everything you need to know about cybersecurity training, why it is important and how to implement it.
Businesses rely heavily on technology, which brings a lot of value and benefits; however, this also means that cybersecurity needs to be moved to the forefront of employee training to protect your business, staff, and customers.
This guide will review what cybersecurity training is and how you can implement it into your training strategy.
Training for cybersecurity should be implemented swiftly and cover a broad range of potential vulnerabilities. A company is only as strong as its weakest link. If one employee lacks the right knowledge about cybersecurity it could expose a vulnerability that has devastating effects.
Here is everything you need to know about cybersecurity training to make sure your business is fully secure.
Contents:
- What is cybersecurity training?
- Why is cybersecurity training important?
- How did remote work affect data breaches?
- The initial attack vectors in 2021
- Types of cybersecurity training for your employees
- 10 Tips and best practices
- TEDtalks about cybersecurity
- A list of free and paid online courses
What is cybersecurity training?
Cybersecurity training is a type of training that focuses on educating staff about potential IT risks and vulnerabilities. It gives people the ability to identify any security threats that could happen when working online and with computer systems.
Cybercriminals use a variety of sophisticated methods to hack into systems with newer methods being created all the time.
To limit the risk of exposure, employees need to be trained in identifying issues, protecting sensitive information, and mitigating the chances of criminals accessing personal information and accounts.
Many security breaches stem from human error. According to Verizon 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report 85% of breaches involved a human element, while 61% involved credentials.
Threats to your business can come from phishing emails, visiting websites, and even in the physical world via social engineering.
By developing a proper cybersecurity training strategy for your business you can teach your employees about their role in protecting sensitive company information.

Training evaluation form
Get a handy printable form for evaluating training and course experiences.
Download nowWhy is cybersecurity training important?
Protecting yourself from cyber criminals who can harm your business is the key reason for cybersecurity training.
Criminals are looking for ways to access company finances, private client information, and extort money from businesses. Money is often the motive and the cost of a data breach can be devastating.
According to IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021, the global average total cost for data breaches rose to $4.24m, which represents a 9.8% increase compared to 2020. Overall, it took an average of 287 days in 2021 to identify and contain a data breach, which was seven days longer than in the previous year.
The 2021 report showed that the United States suffered the highest cost for data breaches two years in a row, rising to $9.05 million from $8.64 million in 2020.
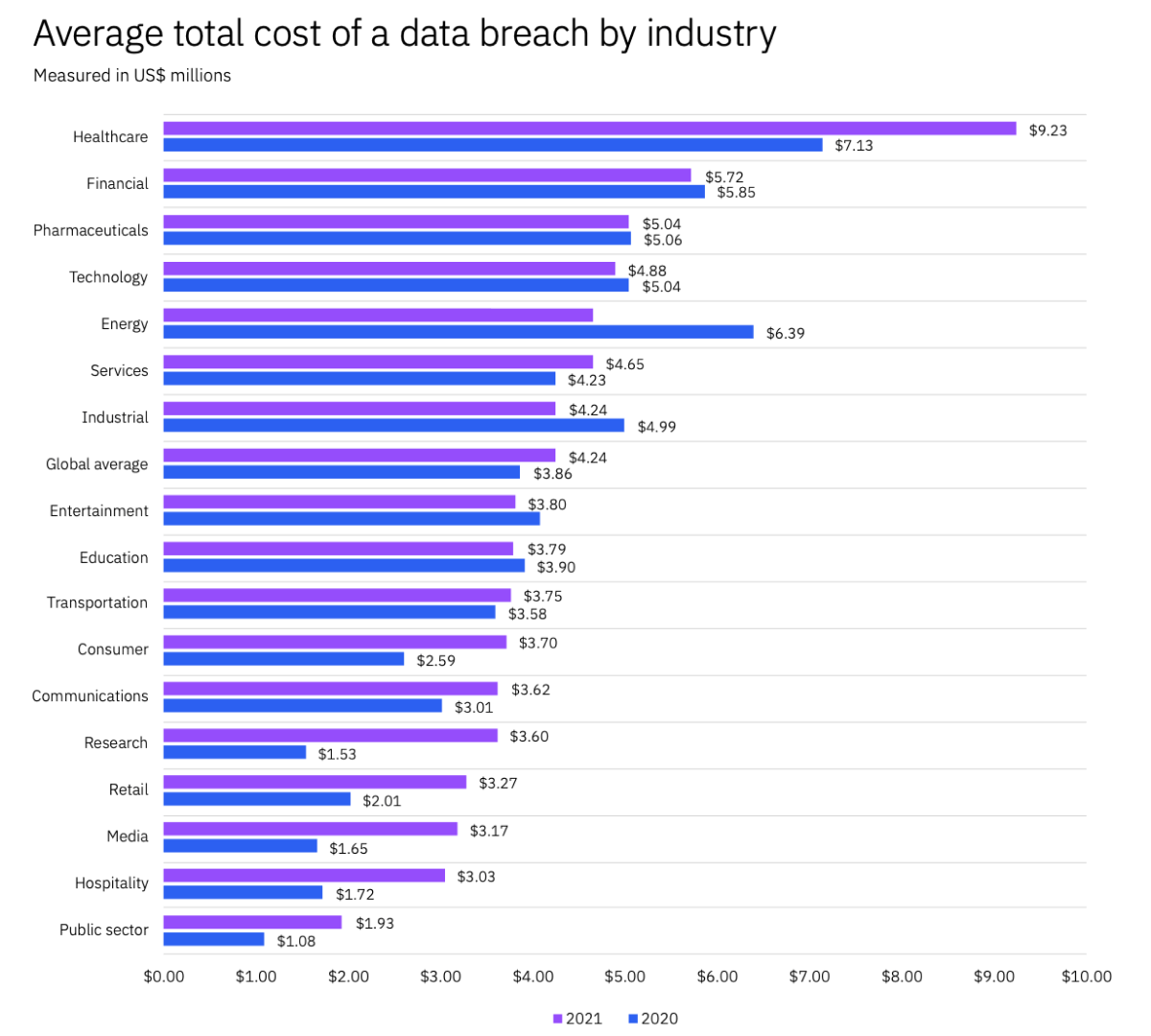
The five industries in 2021 with the highest average data breach costs were:
- Healthcare
- Financial
- Pharmaceuticals
- Technology
- Energy
The healthcare industry has consistently suffered the highest average data breach costs for the past seven years. On average, it cost the healthcare industry $9.23 million, which was a 29.45% increase from the previous year and double that of the global average.
Healthcare, consumer, communications, research, media, retail, and hospitality have all seen a huge increase in average cost, in some cases even more than 50%, which highlights how dangerous cybercrime can be.
Based on the increases in costs associated with data breaches, cybersecurity training needs to be at the forefront of employee training for businesses to help reduce risks of attacks and high costs.
How did remote work affect data breaches?
Remote work led to a $1.07 million (24.2%) higher cost of data breaches in companies where it was a factor, which was 17.5% of organizations. Additionally, organizations with more than 50% remote employees spent an extra 58 days identifying and containing breaches, compared to less remote work-orientated organizations.
The rise of remote working has lead to more worries among employers as they believe responding to a breach will be more difficult.
The initial attack vectors in 2021
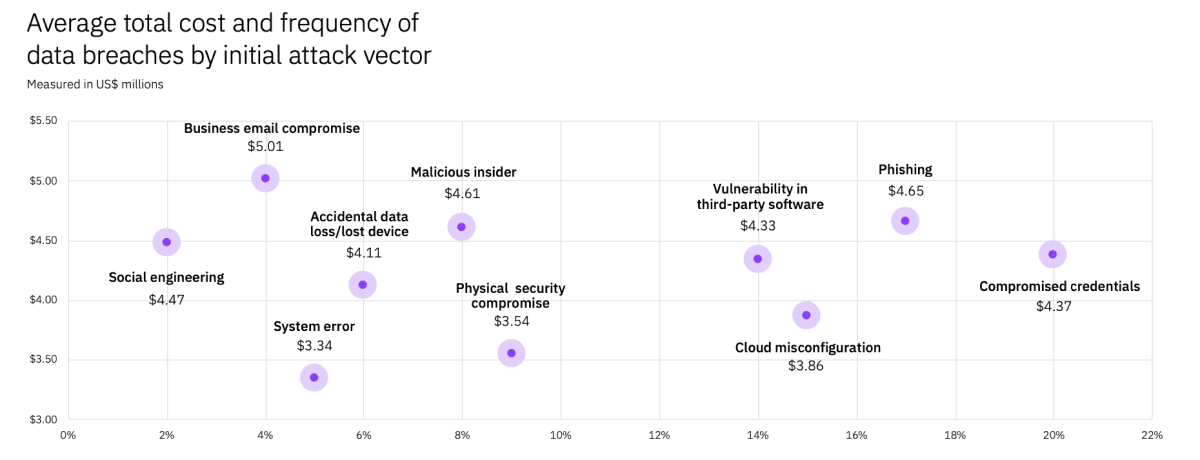
The main three initial attack vectors for data breaches in 2021 were compromised credentials (20%), phishing (17%), cloud misconfiguration (15%).
Attack vectors by cost:
- Email compromise – $5.01 million (4% of cases) – highest average total cost!
- Phishing – $4.65 million (17% of cases)
- Malicious insiders – $4.61 million (8% of cases)
- Social engineering – $4.47 million (2% of cases)
- Compromised credentials – $4.37 million (20% of cases)
- Vulnerability in third-party software – $4.33 million (14% of cases)
- Accidental data loss/lost device – $4.11 million (6% of cases)
- Cloud misconfiguration – $3.86 million (15% of cases)
- Physical security compromise – $3.54 million (9% of cases)
- System error – $3.34 million (5% of cases)
As you can see the root causes of data breaches vary quite a lot. Criminals have plenty of methods they can use to try and infiltrate your network.
Most data breaches are financially motivated, accounting for 53% of all attacks, according to the IBM report, and almost 75% according to the Verizon report.
The collected data on the effects of cyber attacks shows that cybersecurity is more important than it has ever been. Since many businesses are transforming into a hybrid workplace with employees continuing to work remotely, more businesses are developing a bigger digital presence, thus increasing their risk for cyber attacks. Unfortunately, malicious attacks are targeted at businesses of all types and sizes, so regardless if you have 5 or 5,000 employees, cybersecurity training is worth the investment.
Types of cybersecurity training for your employees
Investing in cybersecurity is vital for all businesses and your staff needs access to a proper training program.
To deal with new threats created by cybercriminals your cybersecurity training needs to be kept up to date. This includes reviewing your training materials and continuously updating the content.
There are different training methods available that include simulating attacks, building awareness of common and uncommon attacks, and detailed reporting.
The list of training programs below can help you introduce cybersecurity training to your employees. Cybersecurity is an ongoing problem and it will require frequent refreshers as often as every quarter to ensure your team is prepared against new attacks.
1. Cybersecurity Awareness Training
The basic form of cybersecurity training focuses on raising employee awareness of potential threats.
It can be built into the employee onboarding process for new hires and rolled out to current team members as well.
It’s important to communicate each individual’s responsibility in protecting your company’s data.
There are legal obligations when dealing with customer information and it is a crucial part of every employee’s job to protect this information.
Awareness training includes:
- Email security training
- Internet security training
- Information sharing procedures training
- Basic anti-social engineering training
Common cybersecurity crimes such as social engineering, phishing, and web-based risks may seem obvious but it’s important to cover. Employees need to know how to identify a potential threat and who should be alerted within your organization.
There are plenty of free online training courses available to bring your employees up to speed with the latest cybersecurity issues. Courses are available from reputable organizations as well as government institutions. You can also create your own security courses if you have a learning platform.
There is a list of free and paid courses attached to the bottom of this article to give you a good idea of what is available. Choose the courses that have been updated to include the most recent information on new and emerging threats.
2. Specialised Cybersecurity Programs
There are more advanced programs available that could be ideal for your IT team and roles like security analysts.
These programs help employees to develop a deeper understanding of cybersecurity while giving them the necessary skills to build their defense.
This training can be related to:
- OWASP Top Ten
- CWE/SANS TOP 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors
- DevOps training for secure operations for cloud and deliveries. The CSA training
- Network operations training
- Whitehat hacking and penetration testing training
- Operating system (OS) security training for system administrators
By sending your staff to a virtual or in-person boot camp they can be trained in a broad range of security measures.
Bootcamps are the most comprehensive way to develop professional skills in cybersecurity since it includes vulnerability assessments, data security, and penetration testing. These programs are designed to teach computer science principles and students can get hands-on experience dealing with cyber attacks.
There are all-inclusive training plans available that you can enroll your entire workforce in. These plans will focus on providing all the information necessary for the different roles in your business.
General employees can undertake the basic program while IT and cybersecurity experts can be enrolled in the advanced programs.
3. Compliance security training
Privacy is crucial in this modern technology age. Governments try to protect privacy for their citizens by creating new laws and regulations.
EU GDPR in Europe and The Privacy Act of 1974 in the US regulates data collection and usage. Businesses also need to be aware of what they are collecting, where and how they store and use it.
You need to check the laws for every country you operate in to make sure your business and website meet the set regulations. Privacy laws can also vary between industries with some subject to more rigorous regulations.
Alongside your cybersecurity training, your employees should also undertake compliance training.
Data protection training helps to improve staff knowledge on things like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA), if appropriate for your industry.
According to IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 compliance failures was the top cost amplifying factor among all 25 cost factors. The high level of compliance failures led to a 51.1% increase in the average cost of a data breach compared to low levels of compliance failures.
Standards and regulations you may need to know about include:
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA)
- Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA)
- Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Information Security Management Standard (ISO 27001)
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
- Social Security Act Section 1106 (SSA 1106)
- ISO/IEC 27017
- ISAE 3000 & SOC 2

Training evaluation form
Get a handy printable form for evaluating training and course experiences.
Download now10 Tips and best practices
1. Inject Cybersecurity into your work culture DNA
Encourage employees to follow cybersecurity initiatives and reward them for doing so.
Report successfully prevented incidents, phishing emails, found bugs, and vulnerabilities. Learn from them and especially learn from your mistakes.
Establish an incentive program for developers and reward them with bonuses or extra holidays if they find a bug or vulnerability.
And of course, talk about cybersecurity via communication channels and your in-house messaging.
You can set up counters for “days since the last accident/incident”. Encourage people to focus on this matter and don’t let it get to zero.
2. Lead by example
Leadership must set an example and share the same responsibility as the rest of the employees.
If you ask employees to act according to the policies but ignore them yourself, people will not be as vigilant.
The same goes for consequences. They must be equal, no matter what position a person holds.
3. Adopt a zero-trust security model
A zero-trust security model is an approach to organizational security based on the “never trust, always verify” principle.
In this model, all devices are treated as untrusted by default no matter where they are located or how they are connected, even if they were previously verified.
This model will help your organization prevent unauthorized access to any sensitive data. This is especially important if your organization heavily relies on remote work.
4. Educate your employees in cybersecurity
Employee error can cause cyberattacks against your business. Remember, in 2021, 85% of cyberattack cases involved an employee error.
By training every employee in cybersecurity you can teach them skills and raise awareness of potential threats.
Use this list of practices and training to protect your business against cybercrimes:
Protect from phishing
Hackers send out convincing emails which are known as phishing. They want to convince you to click on a link that can give them access to your computer systems.
Look out for emails from unknown or unfamiliar senders and emails with questionable links.
Don’t interact with the email but let your IT team know it’s been received.
Use strong passwords and change them regularly
Never share your password with anyone including work colleagues.
Create a memorable password that contains upper and lower case characters, numbers, and special characters.
Password manager applications can be used to help store complex passwords especially when you change them frequently.
Keep security software updated
Regular updates are sent out for most software to help keep your security up-to-date, otherwise you could be leaving yourself vulnerable to attacks.
Software companies work hard to counter any new cybersecurity threats so it’s important to update when they become available.
Introduce multifactor authentication for logins
This adds a second layer of security to your accounts. Cybercriminals who gain access to stolen passwords will find it harder to hack into accounts with multifactor authentication.
Multifactor authentication can come in many forms, including physical security keys or push notifications to a mobile phone.
Install virus protection software and firewall
Malware and virus protection software will sweep your databases for any malicious software and inform you of any potential threats.
The software is capable of removing unwanted malware and helping to keep the business safe.
Firewalls are an excellent defense against cybercrimes. They help to prevent unauthorized persons from accessing your files, websites, and mail services.
This is something that employees should have on their personal computers as well, particularly if they conduct work at home.
Use secure Wi-Fi and VPNs
When you first purchase an internet package make sure to use a reputable company that can provide secure and encrypted Wi-Fi solutions.
If some of your staff works remotely, they should use a virtual private network (VPN) to help protect the data.
5. Use software to monitor and protect endpoints
Using software to monitor and protect endpoints is especially important for organizations with employees working remotely.
Use the identity and access management (IAM) software to track suspicious activity, react faster threats, and isolate the damage.
6. Establish and set up proper data backups
Securely backing up your data is one way to protect against ransomware.
This type of malicious attack takes your data storage hostage and holds your business at ransom.
Note: It can help if the data is generic. In most cases, it’s a website. But, if the information is confidential and the goal is to blackmail the business by exposing the data, it won’t help. So, encryption is the next step.
By creating a backup either on a hard drive or in the cloud, you will be able to retrieve your data and restore your systems.
Warning: from our experience, skillful attackers will wait until malware or malicious code becomes part of the backup before a strike.
7. Protect sensitive data with encryption
By encrypting your data you can prevent unauthorized persons from accessing the original data.
It’s a highly popular technique and helps store and transfer files safely. Only someone with the decryption key will be able to access the original data.
This practice is crucial for cloud environments and SaaS applications that operate with users’ personal data and profiles.
8. Stress test your security breach response
Form a team of employees responsible for security response measures.
Create and test response action plans to help your business react faster to any vulnerability and data breach to minimize costs in case an attack happens.
According to the IBM report, organizations that have established and tested response plans decrease total costs by $2.46 million compared to organizations without such measures.
9. Invest in regulatory compliance and training
As we stated before, compliance failures was the top cost amplifying factor that led to a $2.3 million or 51.1% increase in the average cost of a data breach between organizations with high levels versus those with low levels of compliance failures.
Meeting compliance regulations and government requirements are needed not just to avoid getting fined, but also to prevent and minimize the losses in case of a data breach.
10. Educate your developers to create secure code and applications
If you create software, you should adopt and align your development process with security standards and best practices.
Review the Specialized Cybersecurity Programs we talked about above.
TEDtalks about cybersecurity
If you enjoy watching detailed and entertaining videos from tech experts, these TEDtalks about Cybersecurity are exactly what you need.
1. Better cybersecurity starts with honesty and accountability – Nadya Bartol
2. Your Human Firewall – The Answer to the Cyber Security Problem – Rob May
3. The Cyber Skills Gap – Chris Silvers
4. Everyday cybercrime — and what you can do about it – James Lyne
5. The Humanity Behind Cybersecurity Attacks – Mark Burnette
6. Where is cybercrime really coming from? – Caleb Barlow
7. The Five Laws of Cybersecurity – Nick Espinosa
8. Trust Sucks – Nick Espinosa
9. Cybersecurity every day – Jaya Baloo
10. Facets and realities of cyber security threats – Alexandru Catalin Cosoi
11. Cyber Self-Defense – Paul Carugati
A list of free and paid online courses
There are a variety of free or paid courses available online. These come with certifications that can be added to CVs and resumes to bolster your skillset.
1. Linkedin Learning cybersecurity courses
Linkedin has hundreds of courses on cybersecurity available on their website. Everything from foundational classes to full certifications.
One of the most popular teachers on the platform is Malcolm Shore, Cybersecurity Expert, Former Director of GCSB and you can find his courses here.
To start you off, the ones we recommend are:
2. Clark State Community College
Clark State offers free cybersecurity certification classes. They offer six different courses with set start dates throughout the year. Students will learn about risk management, security monitoring, network intrusion analysis, and much more.
3. FutureLearn
FutureLearn offers a wide range of courses including an Introduction to Cyber Security which is accredited by GCHQ, the UK government intelligence organization. This course is ideal for beginners and will take you through the basics of cybersecurity.
Take their free introductory courses to learn more about cybersecurity:
4. Coursera
Coursera has an Introduction to Cybersecurity for Business course that’s been developed by the University of Colorado. Coursera charges for their courses but they offer free enrollment and part of the course for free. You will receive a certificate upon completion.
Their courses can be tried out for free and this is a great course for cybersecurity:
Intro to Cybersecurity for Business
5. Cybrary
Cybrary has free and paid courses available for basic and advanced cybersecurity training. The Introduction to IT & Cybersecurity course is perfect for entry-level employees and will help your team develop their skills. There is a certification offered for completing this course which lasts around 1 hour and 41 minutes.
They have lots of courses available but a good one for beginners to try is:
Introduction to IT & Cybersecurity
6. CompTIA
CompTIA offers globally recognized cybersecurity certification and they’re used by many corporations and defense organizations. This is a paid course that costs $370 and there is a test you will need to pass to receive certification.
If you’re looking to gain professional certificates then these two are a good start:
There is also a CompTIA course hosted on LinkedIn:
Become a CompTIA Security+ Certified Security Professional (SY0-601)
7. Sans
Sans offers a boot camp that will teach you everything you need to know about cybersecurity.
The course is designed to benefit beginners and professionals. The boot camp costs $7,270 and you will earn a GSEC certification which demonstrates you are qualified for IT systems roles.
To become a certified cybersecurity professional check out this bootcamp:
SEC401: Security Essentials: Network, Endpoint, and Cloud
8. Udemy
Udemy has many self-paced courses at very reasonable prices. The downside to this is that their courses aren’t accredited. They will be good enough to learn the basics of cybersecurity and help your business protect itself.

L&D strategy framework
You will receive a list of questions along with a spreadsheet template to help you analyse your L&D strategy.
DOWNLOAD FRAMEWORK



