AI in Learning and Development: Hype vs. Reality
Exploring the use AI for effective employee training and development. What’s just hype and what’s not?

The excitement around artificial intelligence (AI) in learning & development (L&D), is growing rapidly, especially at the crossroads with learning management systems (LMS).
AI’s role in L&D represents a significant shift towards continuous learning and innovation, rather than a passing trend.
However, this growth in AI-integrated LMS solutions has also led to a lot of marketing hype, which makes it hard to distinguish real benefits from mere buzzwords.
John McCarthy, an AI pioneer, famously said that once AI starts working effectively, it’s no longer recognized as AI. This reflects the current LMS market situation where understanding AI’s true potential in L&D is crucial.
The goal for this blog is to help L&D professionals navigate the complexities of AI in LMS, enabling them to make well-informed decisions.
Discover:
- How to use AI in Learning and Development
- AI vs. Machine Learning
- The AI in LMS landscape: What L&D professionals should know
- An AI in employee training and development: How to evaluate LMS solutions
- AI in L&D: Hype vs. Reality
How to use AI in Learning and Development
1. What is Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is fundamentally about replicating human intelligence in machines.
Its role in L&D is increasingly significant and diverse.
2. Using AI in L&D
AI’s applications in L&D range from automating administrative tasks to creating personalized learning paths.
The market offers a wide array of solutions, each contributing in its own way to enhance operational efficiency and personalize learning experiences.
These solutions vary from basic machine learning and analytics to advanced AI functionalities.
Application examples of using AI in L&D:
- Personalized learning paths: AI algorithms analyze learners’ performance, preferences, and learning history to recommend personalized courses and materials.
- Adaptive learning systems: These systems adapt to a learner’s needs in real time, offering more challenging or supportive material as needed.
- Predictive analytics: AI can analyze data to predict which learners are at risk of falling behind and suggest interventions.
Chatbots for support and engagement: AI-powered chatbots can answer learners’ queries in real time, enhancing engagement and support. - Content curation and creation: AI algorithms curate and even create educational content tailored to the needs of different learning groups.
- Language processing for accessibility: AI tools convert text to speech or translate materials into different languages, making learning accessible to a broader audience.
Explore other use cases to understand how AI and Machine Learning can create a more data-oriented approach in employee learning and development.
3. AI vs. Machine Learning
Understanding the difference between AI and machine learning (ML) is essential.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, focuses specifically on data analysis and pattern recognition. This distinction is key to navigating the market and cutting through the marketing hype.
We will go into more detail about the difference later in this blog.
4. AI’s growing importance in corporate strategy
Let’s take a look at some compelling data that underscores the impact of AI in the corporate landscape
- A key insight from Gartner:
A Gartner survey highlights that 79% of corporate strategists view AI and analytics as crucial for success in the next two years.

- Future outlook on AI integration:
Gartner also predicts that by 2026, over 80% of enterprises will use generative AI APIs or integrate generative AI in their applications.
- HR perspective on AI adoption:
76% of HR leaders believe that not adopting AI solutions like generative AI for skills and talent management soon will lead to their organizations falling behind.
AI can significantly enhance the efficacy of your earning programs by tailoring them to meet individual learner needs, thus fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
- Personalized learning programs improve employee engagement and enhance retention:
According to a report by Deloitte, personalized learning programs can lead to a 10% increase in employee engagement. The customizability that AI brings to learning paths is instrumental in achieving this uptick.
A study published in the Journal of Applied Psychology found that personalized learning approaches can improve knowledge retention rates by 25-60%.
- AI helps to gain in efficiency:
Research by the Brandon Hall Group shows that organizations employing AI-driven analytics in their L&D strategy witness an increase in efficiency.
In last 20 years there have been a few key points that have advanced our industry and the way learning is leveraged within organizations. The rise of AI is one of those turning points. AI is already here, and it is constantly providing new opportunities to enhance both learning and business results. There are caveats as well; the risks and rewards must both be understood properly. As with any technology, clear goals and benefits should drive the adoption, not the technology itself. ”
– Valamis Chief Visionary Officer, Jari Järvelä.
This growth underscores the evolving landscape and the escalating significance of understanding the nuanced differences between AI and ML as HR and L&D professionals evaluate and adopt new technologies.

Make AI work for you: a simple guide
Insights, hints, and tips on where to start and what to do next. Perfect for organizations looking for direction.
Learn moreAI vs. Machine Learning: what are the key differences?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) often serve as the backbone of advanced learning systems, yet they have distinct roles and characteristics. Here’s an in-depth look at how they differ.
1. Definition and scope:
Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is a broader concept focused on creating intelligent machines capable of simulating human intelligence processes such as problem-solving, learning, and decision-making. The overarching goal of AI is to create systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
Machine learning (ML): ML, on the other hand, is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data. Rather than being explicitly programmed to perform a task, ML systems use algorithms and statistical models to analyze patterns and make predictions or decisions based on data.
2. Learning and adaptation:
AI: AI systems have the capacity to handle new or unforeseen situations via problem-solving skills. They are designed to mimic human intelligence to respond to a variety of tasks.
ML: ML systems improve their performance on specific tasks as they are exposed to more data over time. They adapt by adjusting the underlying algorithms to improve accuracy or efficiency.
3. Goal:
AI: the goal is to simulate natural intelligence to solve complex problems.
ML: the goal is to learn from data to maximize performance on a specific task.
4. Data and performance:
AI: AI’s performance is measured based on the accuracy and efficiency of task completion.
ML: ML’s performance improves with data; the more data it has to learn from, the better it performs.
5. Examples:
AI: in the context of L&D, AI could be used to create a virtual tutor that can interact with learners in a natural, human-like manner, adapting to their needs and providing personalized guidance.
ML: ML could be employed to analyze the learning patterns of individuals, and then adjust the content delivery based on those patterns to enhance learning outcomes.
By distinguishing between AI and ML, L&D professionals can better navigate the technical and marketing terminologies, ensuring they are investing in the most appropriate and promising technologies for their organizational needs and goals.
“The biggest challenge by far is the overinflated hype. We shouldn’t even talk about artificial intelligence — no such thing exists. Machine learning, or algorithm-driven statistical big data analyses, are far less developed in reality than all the hype suggests. To this end, it is especially critical to educate the leadership in companies to understand what machine learning really is.”…“having said that, machine learning and complex algorithmics will be a more prominent part of running business and market analyses in any companies moving forward. Such tools can help business leaders conveniently manage large data sets and provide new and more salient insight.”
– Lauri Järvilehto, founder of the Finnish academy of philosophy and co-founder of the learning game studio Lightneer
The AI in LMS landscape: what L&D professionals should know
AI integration in LMS is centred around practical, immediate solutions rather than just futuristic ideas. This integration is crucial for L&D professionals to understand and leverage.
For instance:
- AI can automate content curation based on individual learning preferences or past behaviours, significantly enhancing the learning experience;
- and AI-powered analytics can provide actionable insights into learner performance, helping in tailoring courses more effectively.
The successful integration of AI in LMS is not just about technology but understanding and leveraging its capabilities to the fullest.
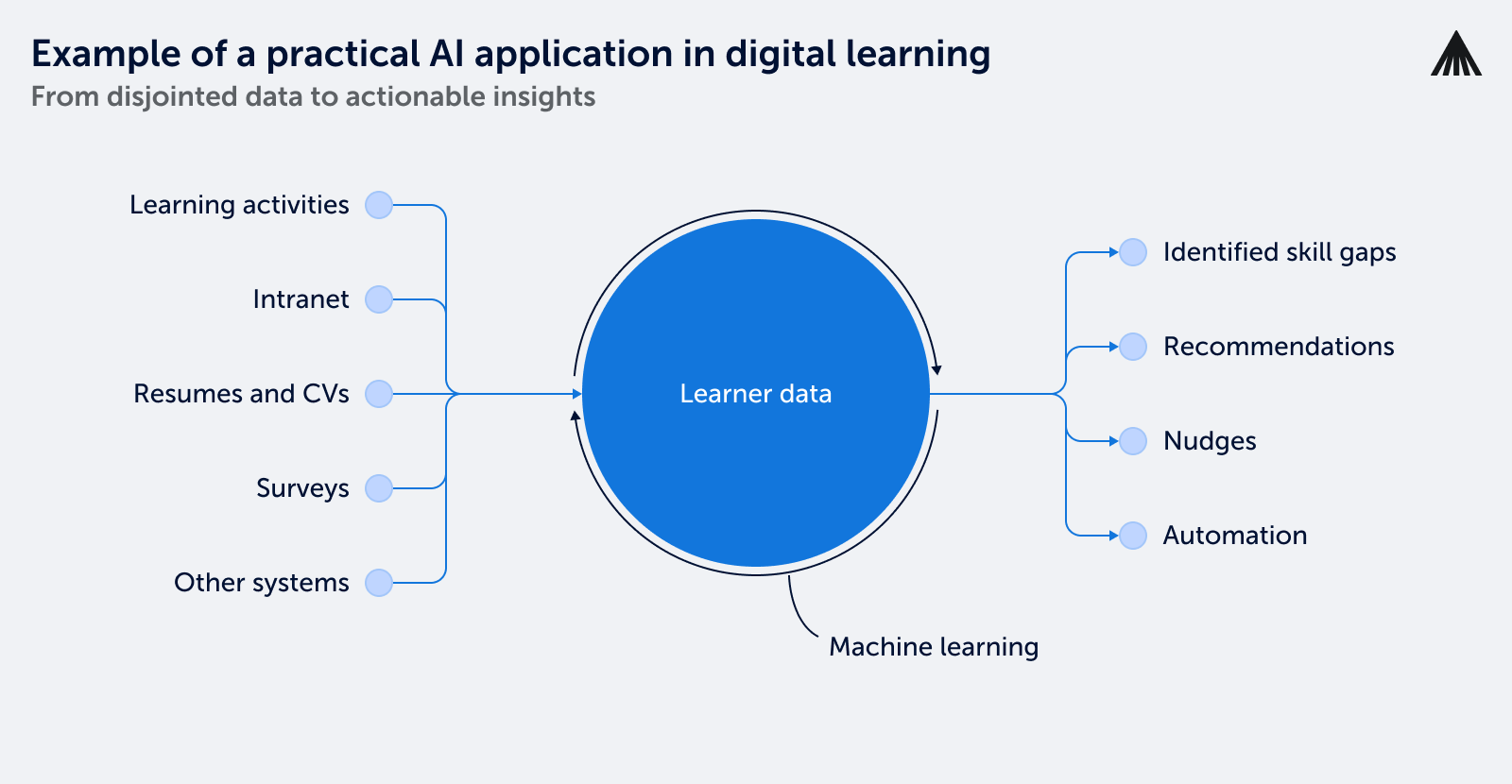
The role of data quality in AI effectiveness
A crucial insight, as highlighted in our latest whitepaper, is the interdependent relationship between the effectiveness of AI and the quality of data it processes.
AI functions as an advanced method for processing data, performing calculations, predictions, and specific actions. However, its functionality hinges on the information it receives, with the accuracy of its results being directly proportional to the data quality.
In the context of organizational learning, the Experience API (xAPI) serves as a key instrument, despite with certain limitations.
While xAPI effectively tracks and stores a variety of learning activities in a Learning Record Store (LRS), it is limited to recording learning within a company’s digital systems, like their internal network, and cannot capture external learning sources.
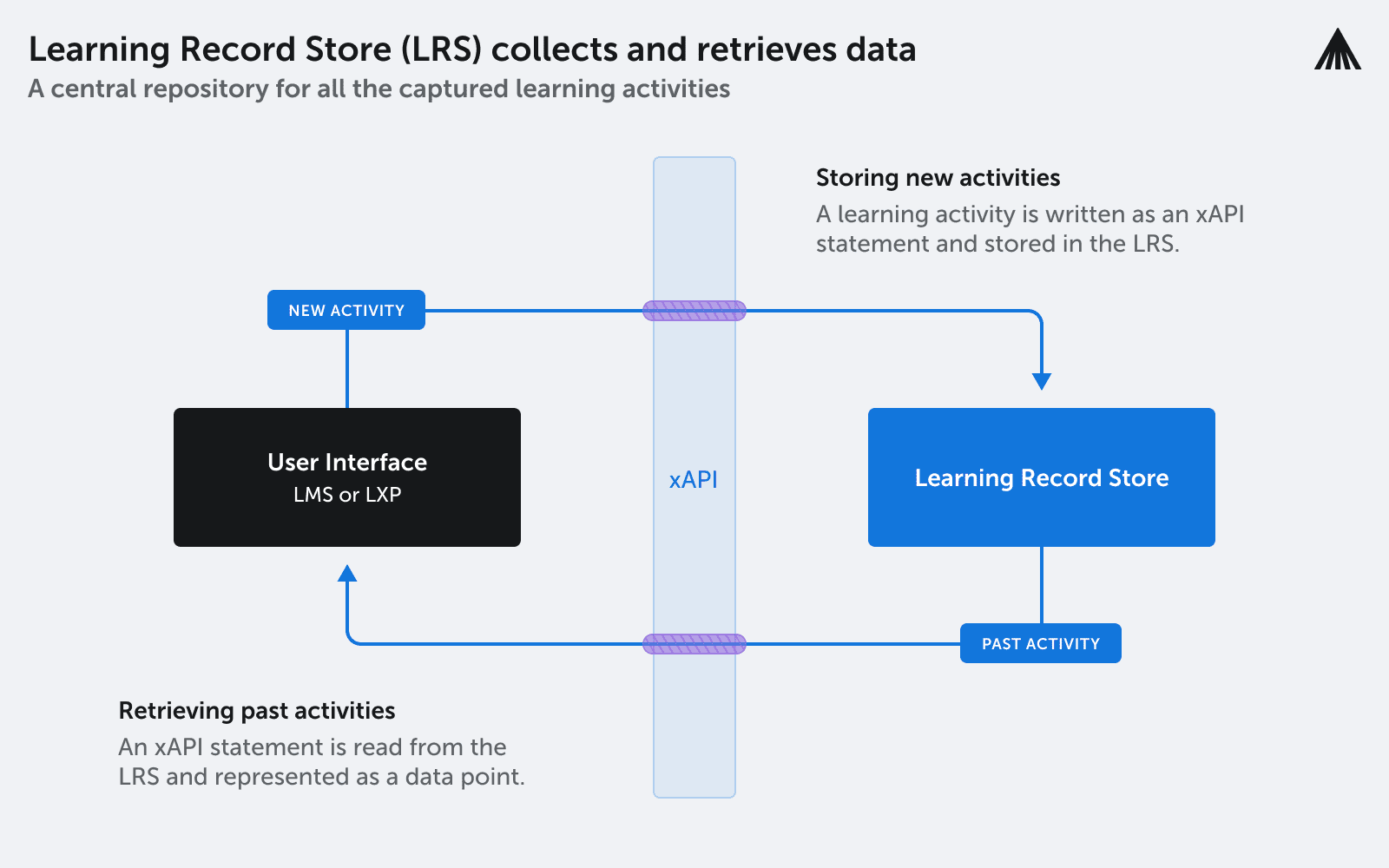
However, combining xAPI data with other business data can be highly beneficial.
Additionally, data from resumes, CVs, and surveys can provide insights into existing knowledge, skills, and certifications.
The overarching goal is to aggregate comprehensive learner data, thereby enabling AI to identify patterns and correlations in learning behaviors across different demographics.
These insights can be instrumental in pinpointing and addressing skill gaps, optimizing processes, and reaping other benefits that significantly enhance business performance. This underscores the indispensable role of quality data in maximizing the potential of AI within the LMS landscape, and by extension, the broader domain of learning and development.

Make AI work for you: a simple guide
Insights, hints, and tips on where to start and what to do next. Perfect for organizations looking for direction.
Learn moreAn AI in employee training and development: how to evaluate LMS solutions
Choosing an AI-driven LMS solution requires a thoughtful approach to ensure alignment with organizational learning and development goals. Here’s a framework to aid professionals in evaluating vendors and finding the right fit:
1. Understand your needs
Identify core objectives: determine the primary business goals you aim to achieve through AI integration in LMS, such as enhanced personalization, improved content recommendations, or streamlined content production.
2. Vendor evaluation
First, inquire about AI capabilities: ask vendors to explain their AI capabilities and how these features can meet your LMS objectives. Seek to understand the technology behind their AI features and how they are applied within the LMS.
Then, request demonstrations: ask for demonstrations of the AI features in action within the LMS, focusing on how they can address your core objectives.
And at the end, conduct pilot testing with real use cases and user groups within your organisation to see how well the AI performs with actual business cases.
3. Align the choice with organizational goals
Long-term alignment: evaluate how well the AI features align with your long-term L&D strategies and broader organizational goals.
4. Evaluate the scalability and future-proof
Explore scalability: assess the scalability of the AI features and inquire about the vendor’s roadmap for future AI enhancements.
Check adaptability: understand how adaptable the LMS is to evolving organizational needs and emerging AI trends in the L&D sector.
5. Inquire about data and security handling
According to our experience, this is one of the important steps when choosing a vendor. Understand how the LMS handles data, which is crucial for effective AI functionality, and ensure that robust privacy and compliance measures are in place.
6. Evaluate vendor support
Assess the level of support and training the vendor provides to help your team effectively leverage the AI capabilities of the LMS.
7. Define success metrics
Establish clear metrics to evaluate the impact and return on investements (ROI) of the AI-driven LMS solution in achieving your L&D objectives.
8. Gather feedback
Ask for references from other customers, especially those with similar L&D objectives, to gain insights into their experiences with the AI features of the LMS.
9. Continuous evaluation
Create mechanisms for continuous evaluation and improvement to ensure the AI functionalities remain relevant and continue to add value as your needs evolve.
To conclude, AI in L&D: hype vs. reality
Hype:
- Marketing overdrive. Companies often get too excited about AI in Learning & Development, especially in LMS. They sometimes make AI sound more amazing than it really is, which can be confusing.
- Misinterpretation and overestimation. Sometimes companies think AI in LMS is going to change everything, but this is often because they don’t fully understand its actual capabilities, leading to inflated expectations and a misunderstanding of its practical applications.
- AI vs. Machine Learning confusion. There’s a prevalent confusion between AI and machine learning. This misunderstanding contributes to unclear perceptions about their respective roles and contributions in L&D systems.
- Overinflated expectations. The impact of AI on learning efficiency and effectiveness is often overhyped. This overlooks the foundational work needed to integrate AI successfully, leading to unrealistic expectations about its potential benefits.
Reality:
- Practical applications. In reality, AI significantly improves learning programs by tailoring them to individual learner needs. It provides valuable data-driven insights, enabling more effective and personalized learning experiences.
- Improved engagement and retention. AI-powered personalized learning programs have been shown to increase employee engagement. Reports and studies we mentioned before show that this kind of learning can make people more engaged and help them remember things better.
- Working smarter. Organizations incorporating AI-driven analytics into their L&D strategies experience increased efficiency. Research by the Brandon Hall Group indicates that such integrations lead to more streamlined and effective learning processes.
- Good data matters. The success and effectiveness of AI in L&D heavily depend on the quality of input data. High-quality, relevant data is crucial for AI systems to provide accurate and useful insights.
- Strategic integration. The successful integration of AI in L&D involves not just technology adoption but also understanding how to leverage AI capabilities in alignment with organizational goals. This strategic approach ensures that AI contributes meaningfully to L&D objectives.
- Upskilling and adaptability. Looking towards the future, L&D landscapes will require continuous upskilling in AI and adaptability to AI-driven trends. This emphasis on ongoing learning and innovation is essential for staying abreast of developments in AI and its applications in L&D.
AI in L&D is a significant advancement, not just a trend. It offers numerous benefits.
L&D professionals play a crucial role in this evolution. It’s essential to move beyond the hype and focus on the real value of AI, making informed decisions in LMS selection.
The focus should be on using AI strategically, carefully choosing LMS vendors, upskilling the L&D team, and keeping pace with emerging AI trends. By doing so, L&D professionals can effectively harness AI’s growing potential.
Turn data insights into actions
Make every lesson count. Data insights from our LMS ensure your team’s development is always on track.
Learn more