Corporate training
Learn what corporate training is and how it can help you to improve employee efficiency and motivation and reduce employee turnover.

In this article, we will discuss:
- What is corporate training?
- Goals of corporate training programs
- Benefits of corporate training
- Examples of corporate training programs
- How to organize corporate training
- Reasons why corporate training can fail
- Corporate training trends 2024-2025
What is corporate training?
Corporate training refers to employee learning and development initiatives that aim to improve various aspects of an organization.
Corporate training is the remit of the HR department or, in larger organizations, a dedicated L&D team.
Their responsibilities include identifying knowledge gaps and training needs, developing and delivering training programs depending on business needs, and creating long-term education strategies for specific individuals and the workforce as a whole.
This can include onboarding new staff, learning new skills, reskilling employees for new roles or upskilling within the existing one, or any other scenario where training can make a difference in the workplace.
When successful, corporate training is advantageous for both management and employees.
- Leadership can improve business operations and enhance workforce capabilities with specific strategic goals in mind.
- Employees can develop new skills and learn knowledge to progress in their careers.

L&D strategy framework
You will receive a list of questions along with a spreadsheet template to help you analyse your L&D strategy.
DOWNLOAD FRAMEWORKGoals of corporate training programs
Corporate training allows organizations to manage the development of their employees.

While specific goals within corporate training vary depending on the organization (and amongst different employees within the same organization), multiple big-picture objectives are consistently present. These include:
- Expanding workforce capability – By developing the knowledge and expertise of employees, organizations can reduce skill gaps and expand workforce capabilities. This could be to improve operations, increase productivity, enhance staff agility, or position the business to take advantage of new growth channels.
- Retaining talent – Investing in staff through corporate training shows the organization cares about its employees and their professional development. This, combined with opportunities for professional growth and internal mobility, allow organizations to hold onto talented employees.
- Building work culture – Corporate training allows an organization to explain, promote, and instill its workplace culture. This could include big picture core values that help achieve the business’s goals or specific expectations from employees joining the company, such as a code of conduct.
- Increase organizational performance – Training staff to be better at their job leads to greater productivity. Corporate training costs money, and when done right, businesses see a return on that investment with increased performance thanks to staff using their time more efficiently.
Benefits of corporate training
In general, there are two main reasons why companies should make use of corporate training programs now more than ever include the influx of new technology and greater marketplace competition.
While new technologies have always facilitated innovation, recent years have seen a significant number of disruptive technologies find widespread use, transforming entire industries. With automation, AI, and a range of other digital technology leading the way, businesses must constantly train staff to remain up to date and reap the benefits.
In the modern business world, there is more competition than ever before, and customers now expect better service. With more choices, businesses are looking to differentiate themselves by offering smooth and personalized customer experiences.
Therefore, organizations must continuously train staff to create the best customer service possible and remain competitive.
So, what other benefits will they get by focusing on corporate training and employee development?

1. Employee development
Corporate training develops employees to remove workforce skill gaps and identify new leaders for smoother succession planning.
With constantly updating digital tools, the half-life of professional skills has dropped significantly, from 10-15 years down to 5 years. Employee development allows organizations to train staff on relevant technical skills that meet evolving business demands
2. Agility
Agility is a commonly desired outcome of corporate training.
Developing new hard skills and knowledge allows organizations to pivot when market conditions change quickly. However, corporate training is also vital to enhance employee soft skills, allowing them to better cope under pressure and adapt quickly, ensuring effective decision-making.
3. Motivation and engagement
Beyond giving staff new skills to improve at work, corporate training and investing in staff can generate motivation and engagement. Surveys show that 92% of employees found successful training increases job engagement. Having a motivated and engaged team leads to better business outcomes.
On the other hand, employee disengagement can become a significant cost center. For example, global research by Gallup found that actively disengaged employees waste the equivalent of 18% of their salary.
4. Reduced employee turnover
Boosting employee motivation and engagement are critical factors in reducing turnover. Studies show employee engagement reduces voluntary turnover by 31%.
Further research found that 94% of employees would remain at a company for longer if they invested in their L&D.
Reduced employee turnover helps organizations retain talented staff, maintain consistent operations, and lessen the cost of hiring new staff. The Center for American Progress previously found the cost of replacing an employee can rise to as high as 213% of the employee’s salary.
5. Hiring
This doesn’t mean hiring is not a vital part of all growing businesses.
Strong corporate training processes show an organization values its staff and works to develop them as individuals. This can boost the company’s reputation helping to attract stronger candidates.
6. Efficiency and productivity
Corporate training and improving employee performance directly affect a company’s bottom line.
Organizations can see significant ROI on corporate training spending when executed correctly, thanks to greater efficiency and enhanced productivity.
Research by IBM found a 10% productivity increase when a team is well-trained. This leads to a 22% faster rollout of new business processes and products. As a result, corporate training can help organizations drive revenue and growth.
Examples of corporate training programs
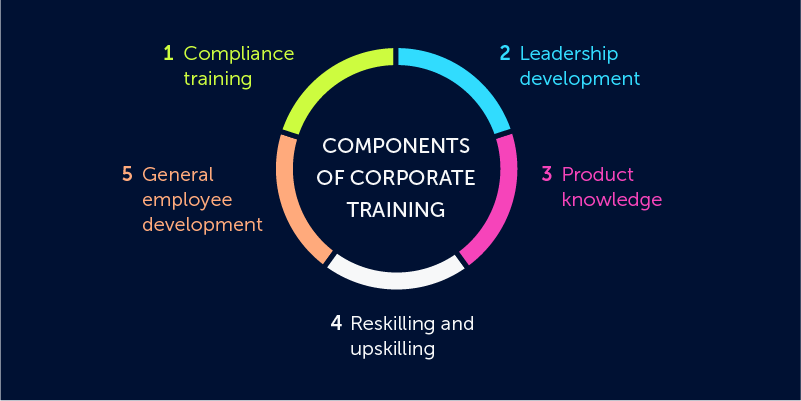
1. Employee onboarding
Onboarding training aims to integrate new employees within the organization as quickly as possible.
It typically includes general information about the workplace, such as IT logins or corporate policies, and the specific knowledge employees need for their roles, like the resources to complete their responsibilities or the team’s communication channels.
Onboarding is also a great opportunity to impart the company’s core values and culture, setting the expectations for all new workers.
Smooth onboarding procedures can reduce employee stress when joining a new company and hopefully quickly make them feel comfortable in the workplace. For companies, it can help minimize transition time such that employees begin creating value as soon as possible.
Check out our articles on the Onboarding process and Onboarding checklists for more information.
2. Compliance training
Typically part of onboarding, compliance training is a formal program focusing on the company’s policies and rules.
The specifics of compliance training depend on the type of industry and role. However, it generally includes health and safety, a code of conduct, data protection, workplace harassment policy, diversity training, and privacy protection.
Compliance training ensures the baseline expectations regarding behavior are made explicit to all employees. This can prevent employee issues in the workplace and offer the company legal protection.
Check out our article on the Compliance training and discover tips and best practices.
3. General employee development
Employee development refers to training that focuses on improving staff capabilities.
Educating staff is advantageous for everyone involved. For example, helping leadership build a better workforce to optimize operations and assisting employees in their development personally, potentially opening doors to new professional opportunities.
Check out our articles on Employee Development Areas and Employee Development Plan.
4. Leadership development
Leadership development looks to increase the leadership skills within the workforce through various processes. This could be internal via mentorship programs or sending staff off-site for seminars or conferences to develop their leadership capabilities.
Good managers and supervisors look for employees with the potential to excel in leadership roles.
Leadership development helps ensure an organization has ready-made replacements should key staff members choose to retire or leave. Impactful leadership development programs also help retain ambitious and talented employees who can see a clear career path at the company.
5. Product knowledge training
Outside the product team, many others in the company need deep knowledge of the goods or services provided. For example:
- The marketing team must understand the product to attract future customers
- The sales team, which directly communicates with the customers, needs to be able to talk confidently about the product and what it can and can’t do
- The customer service team needs to know the product in and out to help customers with their issue
While this may be harder for certain sectors (e.g., tech, science, etc.), offering product training to everyone at an organization helps everyone perform their role. It can also inspire employees to become more involved and motivated, bring new ideas from unlikely sources, and bring everyone together to improve working relationships.
6. Reskilling and upskilling
Two closely related ideas, reskilling refers to training employees for a new role, and upskilling is developing new skills for an employee’s existing position.
With the influx of new technology and a reduction in the half-life of skills, both reskilling and upskilling are seeing significant interest.
Reskilling allows employees to retrain and change their profession at an uncertain time when technology is making a growing number of roles obsolete.
Upskilling keeps staff up-to-date on the best practices available to perform their role. Both allow organizations to maintain an effective workforce and adapt to changing times.

How to conduct a skills gap analysis and what to do next
Start building your foundation for strategic workforce development.
Download guideHow to organize corporate training
Let’s take a look at the various techniques that are common in corporate training:
1. Traditional classroom training
Instructor-led, in-person training is still used in many companies.
While it might not be ground-breaking, it is easily customizable, offers plenty of opportunities for various types of assessments, and has the advantage of being familiar.
It is not scalable, and space is limited to how many learners can fit into the physical classroom, so there are limitations to these types of programs.
2. Virtual instructor-led training
This updated version of the classroom training offers a lot of advantages that in-person training lacks, with relatively few disadvantages.
More people can attend training sessions, as space is no longer limited to a physical classroom.
Sessions can be recorded and reviewed by future learners, and it offers a way for people to continue learning without interruption in the ‘new normal’ of all-remote work.
Although this requires all learners to have the correct equipment and connection speed, one main disadvantage is that learners might feel disengaged with all-online learning, so instructors would have to contend with that. In this type of training, no matter how many learners are involved, you will only have a finite number of instructors, so the training may be less effective.
3. Online learning
Online learning is a bit of a catch-all term and can be used to refer to any resource online that contains educational content, such as online courses, quizzes, games, discussion boards, videos, and assessments.
This has been the fastest-growing area in corporate training, with many companies dedicating a lot of energy to developing their online learning tools, as they are scalable, accessible, and serve the users at the point of need.
For this learning the need in modern technology is essential. Check out more about LMS and its capabilities.
Lacking employee engagement?
Our approach makes learning more interesting by using different ways to keep learners motivated and inspired, beyond just captivating content.
Learn more4. Blended learning
This type of learning marries classroom-based and online learning, taking the best of each type and delivering it to the learner.
This approach tends to be the most successful, as it is more scalable, accessible, and flexible, and it is more able to meet the needs of diverse students.
This approach requires a solid infrastructure, learners who are comfortable with technology, and instructors who are able to make the most of this training approach.
Learn more about blended learning in our article.
Reasons why training can fail
While corporate training has considerable merit, it can be challenging to translate programs into meaningful results. Research shows:
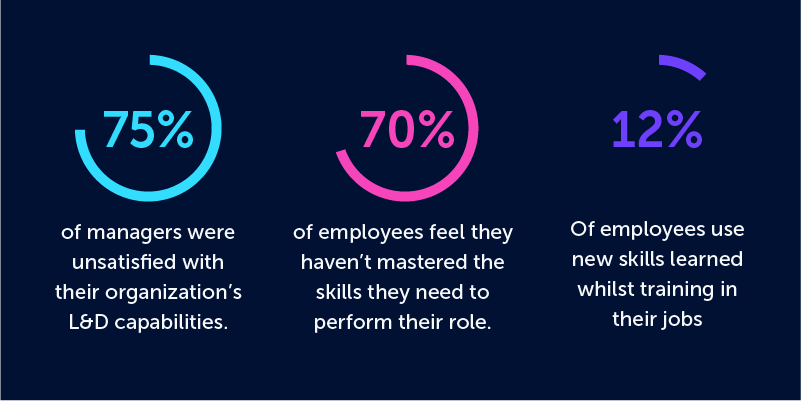
- 75% of managers surveyed were unsatisfied with their organization’s L&D capabilities.
- 70% of employees feel they haven’t mastered the skills they need to perform their role.
- Only 12% of employees apply new skills learned during training programs top in their job.
There are many factors for the lack of success in corporate training. However, common reasons for failure include:
- Failing to understand corporate training objectives or improperly analyzing learning outcomes and results.
- A lack of investment from leadership making corporate training seem like a cost center rather than an opportunity.
- Corporate training that becomes too generalized and lacks the specificity to make a real difference to an individual in a particular role.
- Staff are too afraid of failure and unwilling to implement new ideas and approaches discovered through corporate training.
- Tracking programs (i.e., training credits or something similar) turning corporate training into a box-ticking exercise rather than the learning and application of useful skills.
- New skills are quickly forgotten if they are not used soon after training.
Trends in corporate training in 2025
Read more about Learning and Development trends in 2025 in our other blog. Discover the 2025 trends that are shaping the future of workforce skills.

L&D strategy framework
You will receive a list of questions along with a spreadsheet template to help you analyse your L&D strategy.
DOWNLOAD FRAMEWORK



